Nacos源码学习计划-Day15-配置中心-Nacos客户端如何读取的远端配置
ZealSinger 发布于 阅读:252 技术文档
我们知道,我们在使用Nacos的时候,可以在Nacos的管理端处配置对应的配置,然后所有的注册在该Nacos上的服务都会使用该配置的内容,那么我们就可以思考如下几个问题
-
客户端是怎么加载和读取到Nacos远端的配置?
-
Nacos中可以定义多种类型的配置文件,他们的隔离性,优先级是怎么设计的?
-
Nacos远端配置更改之后,客户端是怎么感知的?怎么实现热更新的?
-
Nacos集群下,节点间的配置怎么同步和处理的?
我们的Nacos配置中心模块的主要学习就是从如下几个方向上出发。本篇解决第一个问题:客户端如何加载和读取Nacos的远端配置
客户端如何加载和读取Nacos的远端配置
我们在使用SpringBoot整合Nacos的时候,当我们需要使用Nacos远端配置,我们知道会需要写一个额外的配置文件bootstrap.yml并且加载Nacos的远端配置都是在服务启动之后就能立马加载且支持热更新
很明显,我们需要和分析“注册服务寻找客户端如何注册到Naocs服务端”时一样,从客户端的自动配置入手,如下,我们在Nacos的依赖文件中可以看到有这么一个类NacosConfigBootstrapConfiguration
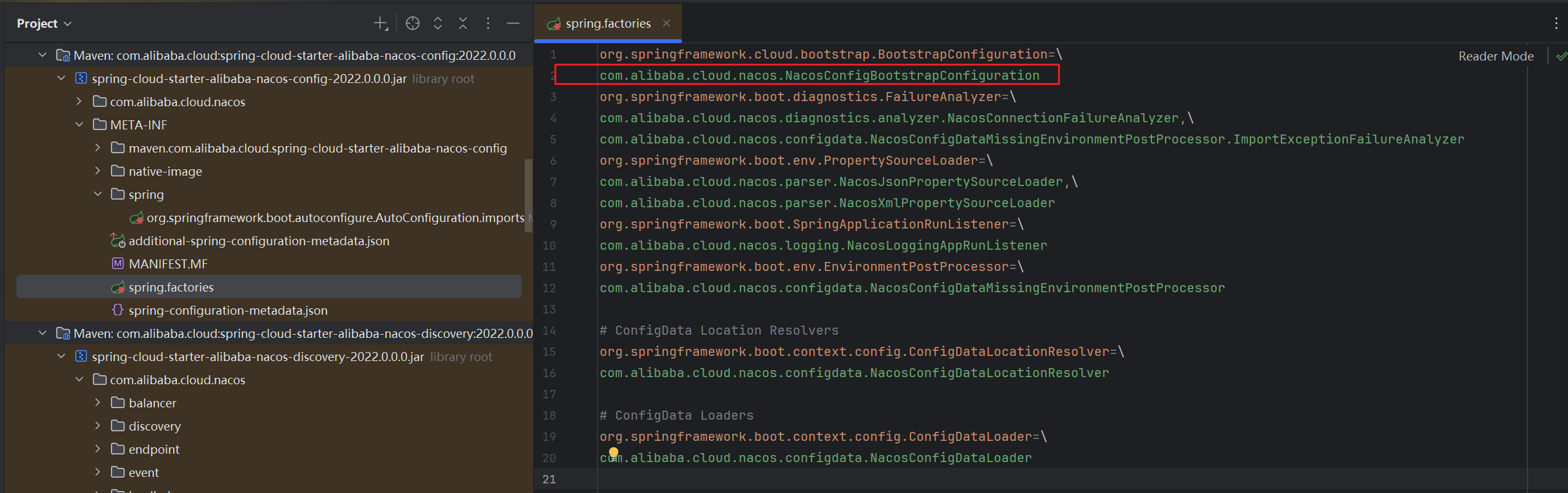
可以看到这个配置类中,定义了四个Bean-NacosConfigProperties ;NacosConfigManager ;NacosPropertySourceLocator ;ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder
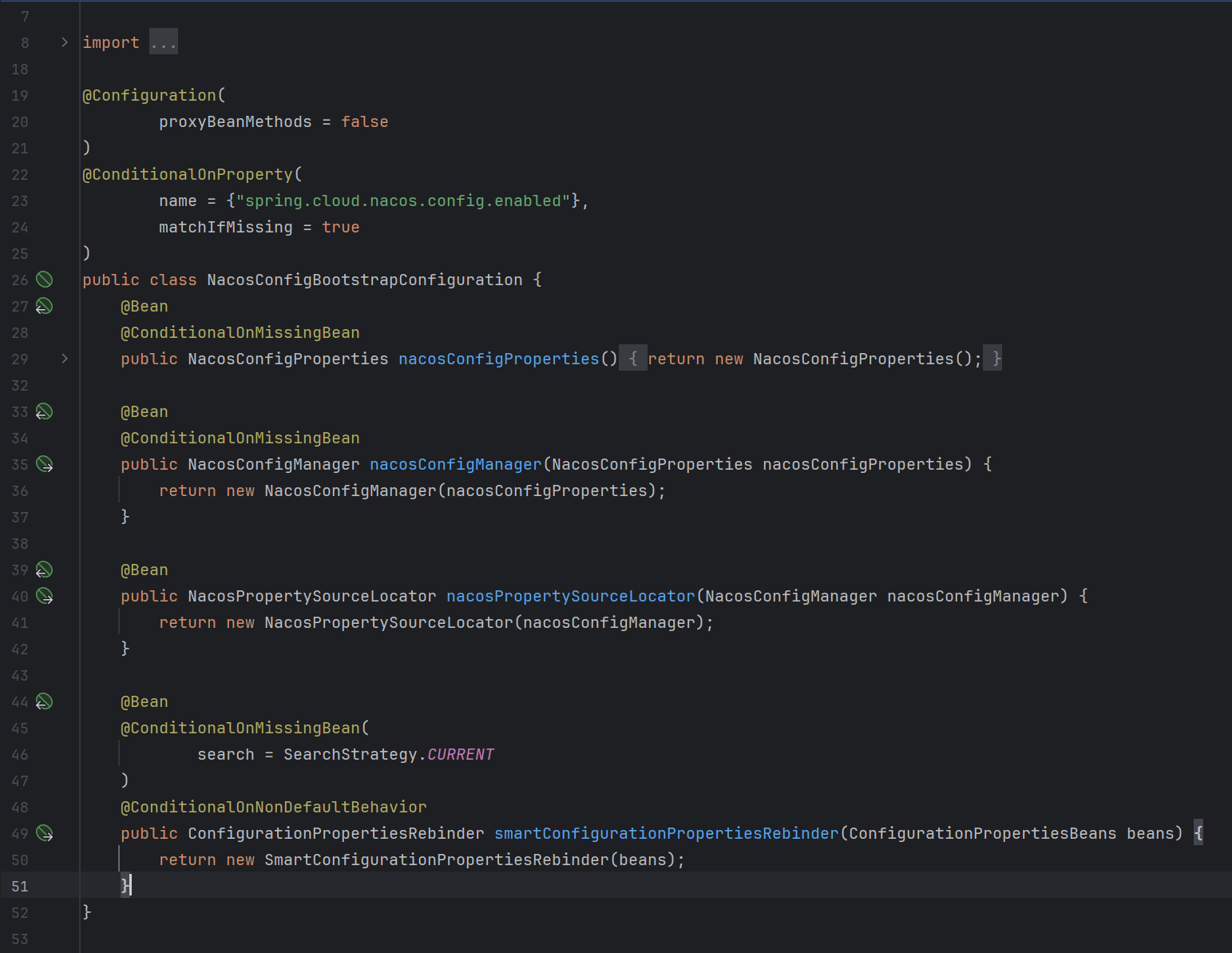
NacosConfigProperties
首先是NacosConfigProperties,从命名来看就知道,这个是Nacos配置的实体类,将一些常用的配置信息封装为了一个类对象,和配置信息相关但和加载读取配置无关
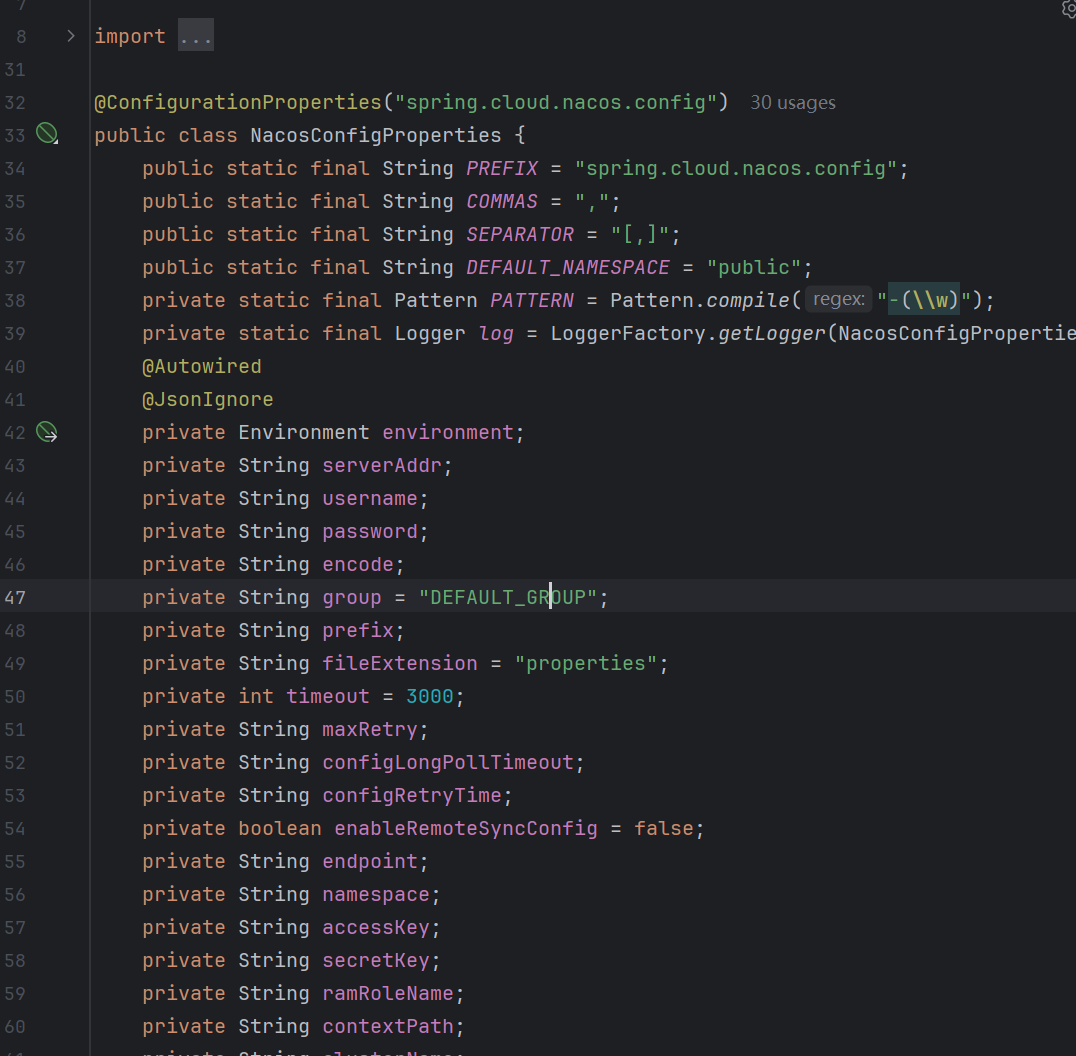
NacosConfigManager
NacosConfigManager主要的有两个成员,ConfigService和NacosConfigProperties,前者为一个和配置操作相关的接口实现类对象,后者为配置对象。
可以看到这个ConfigService的创建还使用了懒汉式的创建方式,NacosConfigManager 是一个配置管理核心组件,主要职责包括: ConfigService提供者: 创建和管理Nacos的 ConfigService 实例,这是与Nacos配置服务器交互的核心接口,主要作用是提供创建/发布/删除配置,而不是指导客户端加载读取配置。
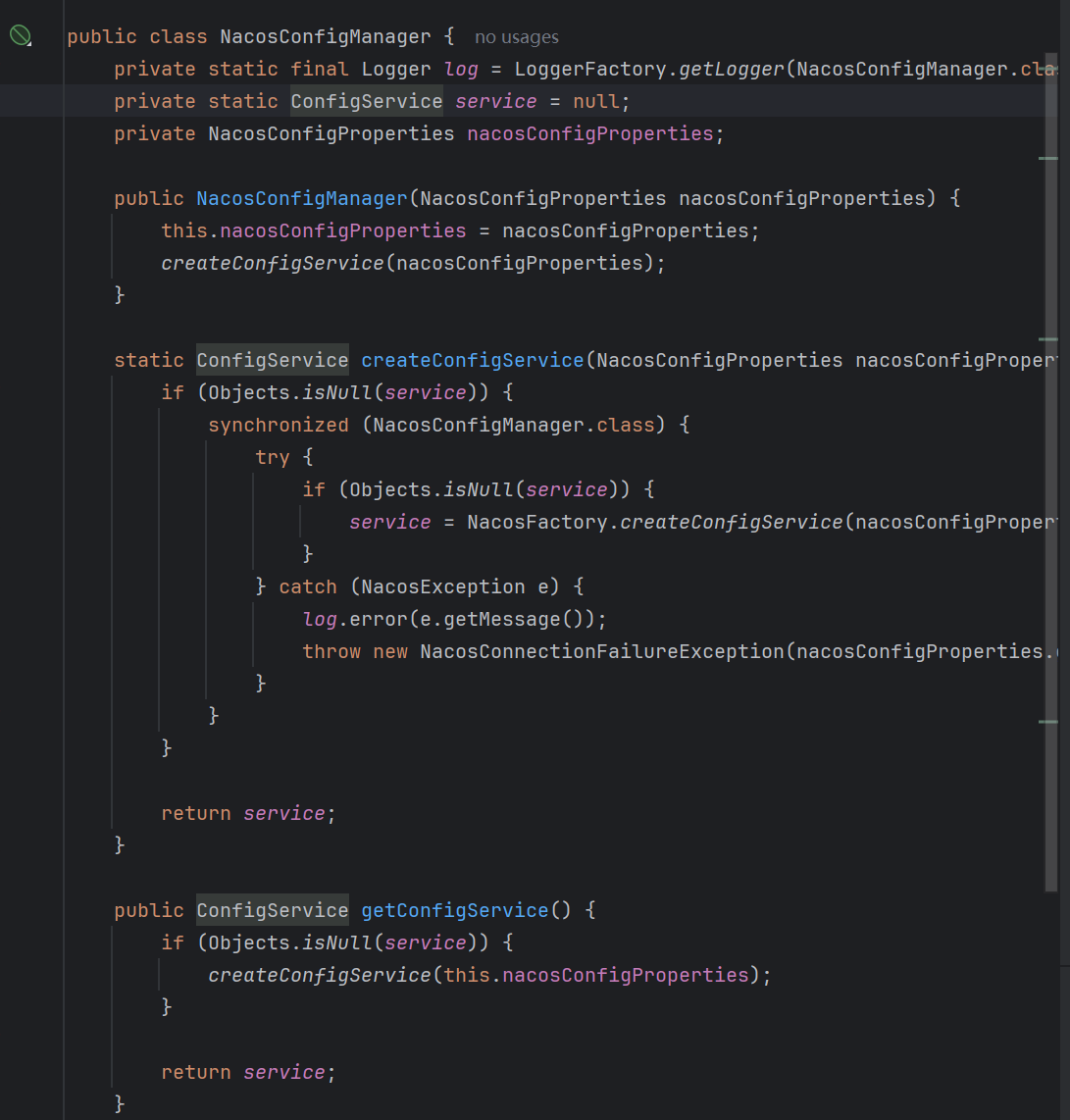
NacosPropertySourceLocator
其实,如果了解SpringCloud配置加载机制的UU,看到这个类的命名的时候,应该由能知道,bootStrap配置文件的加载和读取和这个类八九不离十。
我们来查看一下这个类的源代码,可以看到其内部维护了NacosPropertySourceBuilder ; NacosConfigProperties和 NacosConfigManager,并且该类实现了PropertySourceLocator
后面两个对象我们上面有小分析,我们主要来看其本身的逻辑以及其实现的接口PropertySourceLocator
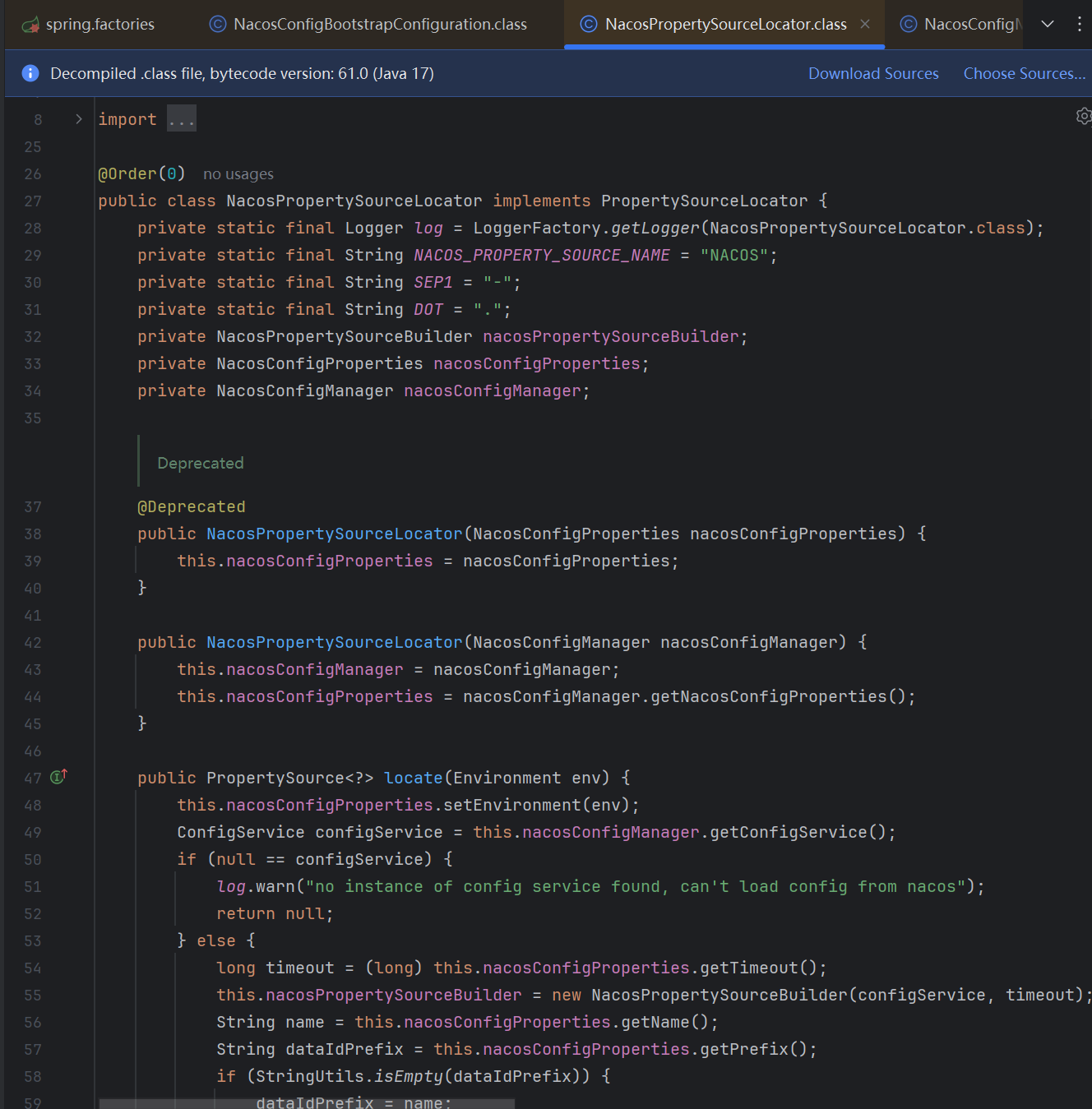
PropertySourceLocator接口
这个接口如果大家没有接触过的话,我们可以现在来看一下,分析一下他的作用,可以看到这个接口内部,有一个default默认方法和一个static静态方法,default方法的内部其实也就是调用static方法,所以可以认定,这个接口只有一个方法locateCollection()
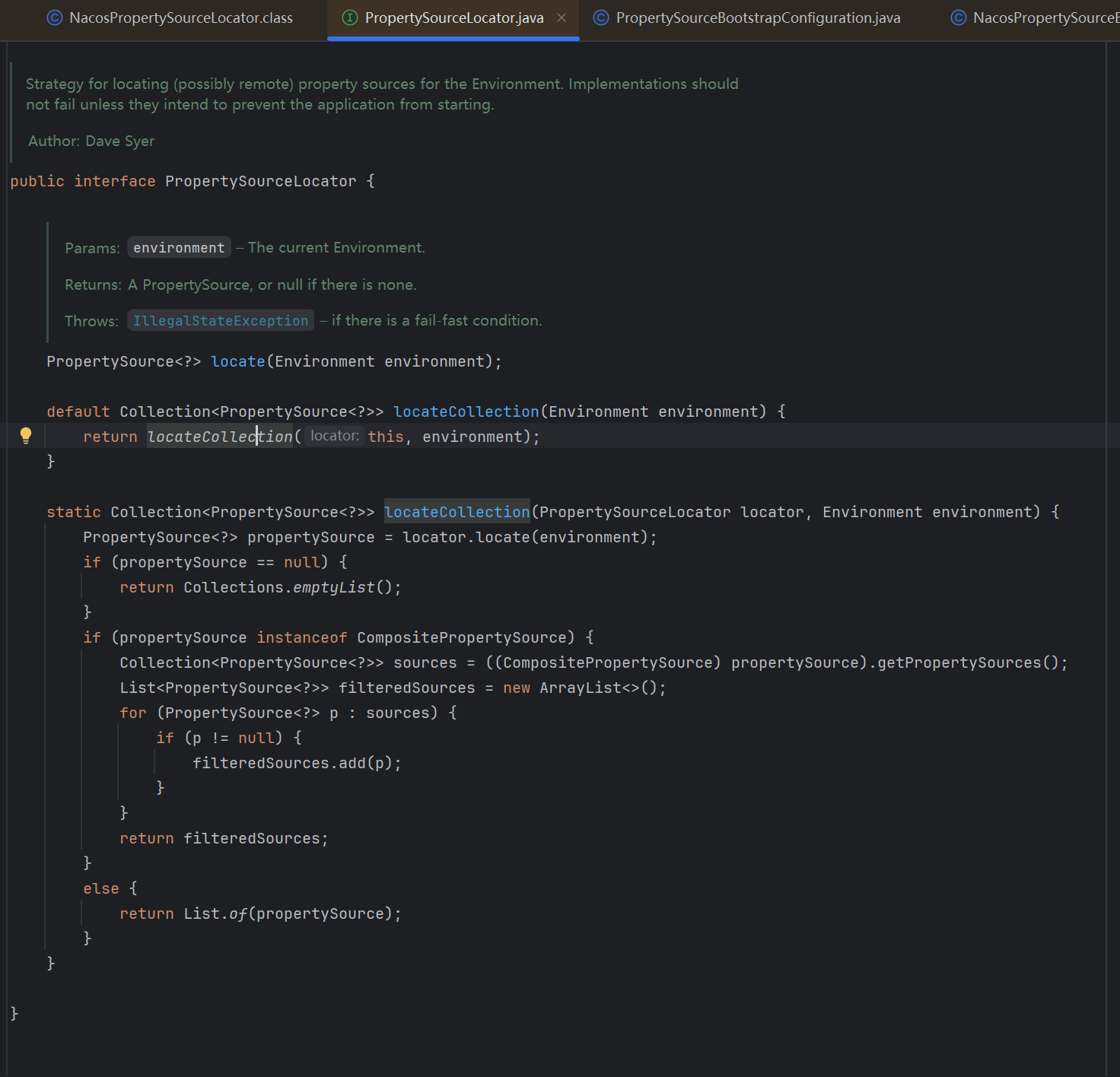
我们看一下这个defalut的这个方法在哪里被调用了,发现只有一个地方调用了,在SpringFrameWork的一个包中的PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration类的initialize方法中被调用
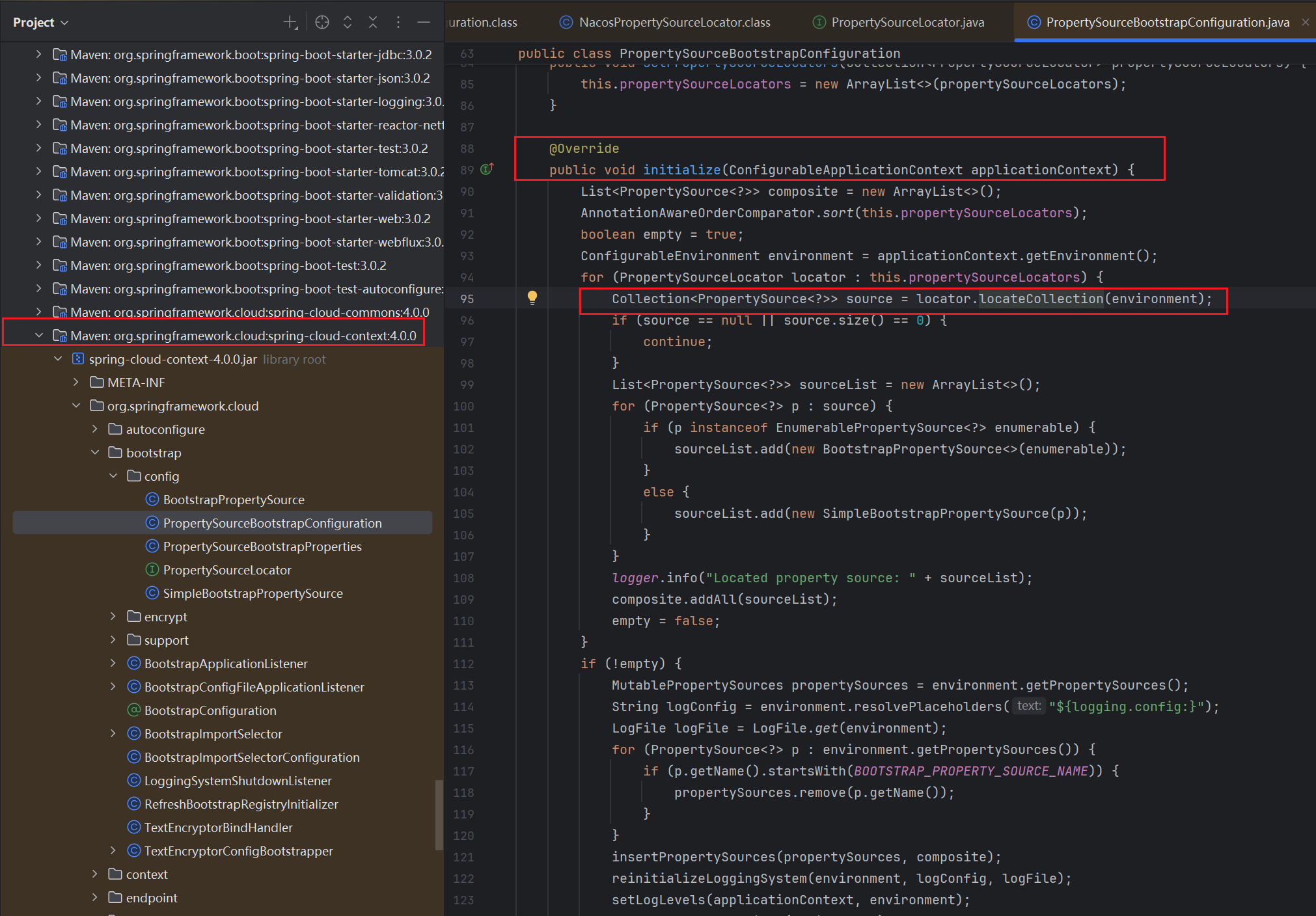
我们查看一下这个initialize被调用的地方,可以发现在SpringApplication中被调用了,看到这里其实已经很明显了,这个接口肯定属于整个SpringBoot启动时候的一个拓展点(类似于Bead前处理器,Bean实例化后处理器,属于启动后的流程内的一个钩子方法)
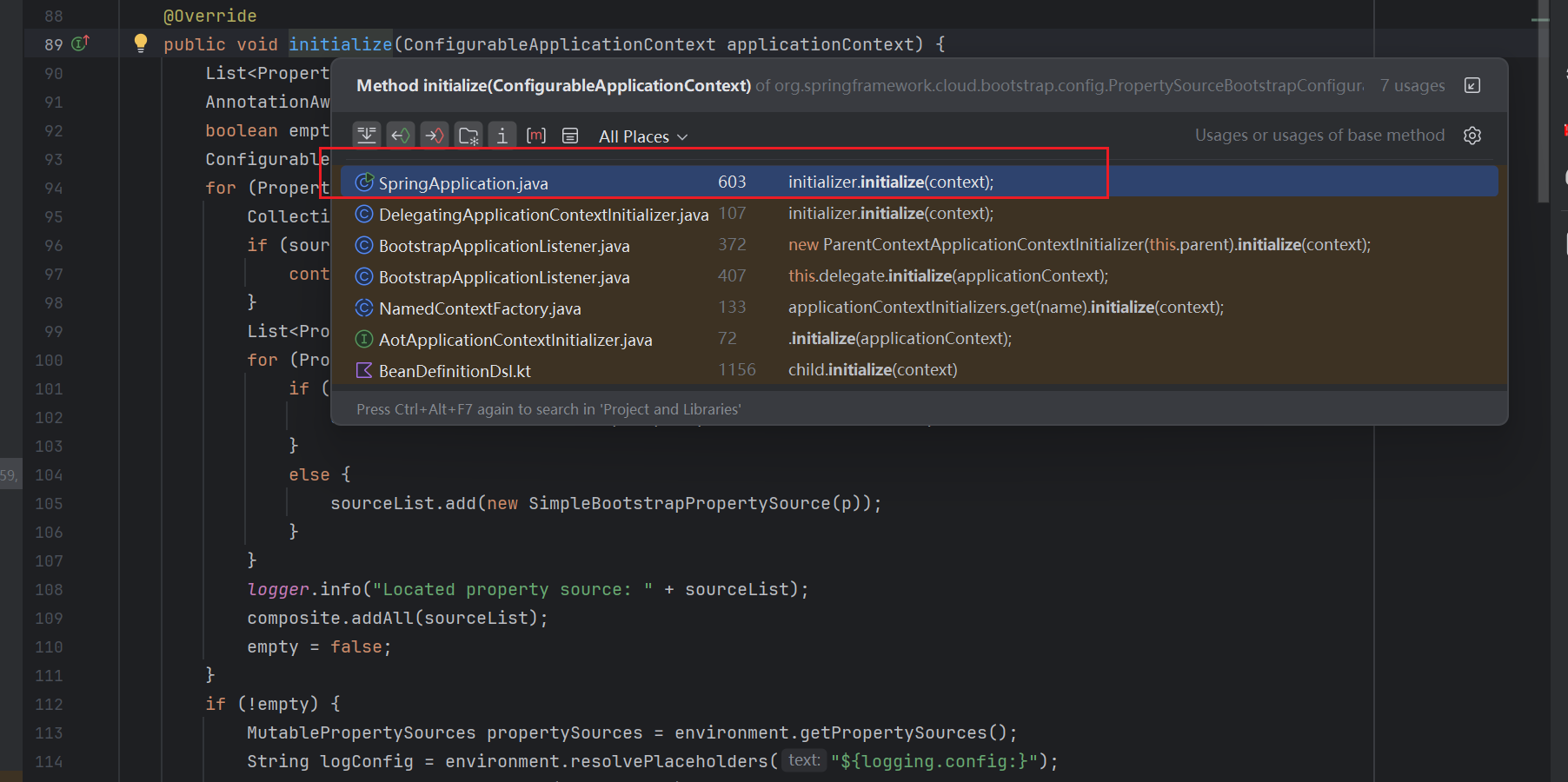
继续往下面跟,在SpringApplication的applyInitializers方法中被调用,该方法又是在同类下的prepareContext方法中被调用,而prepareContext又被同类下的run(String... args)方法调用
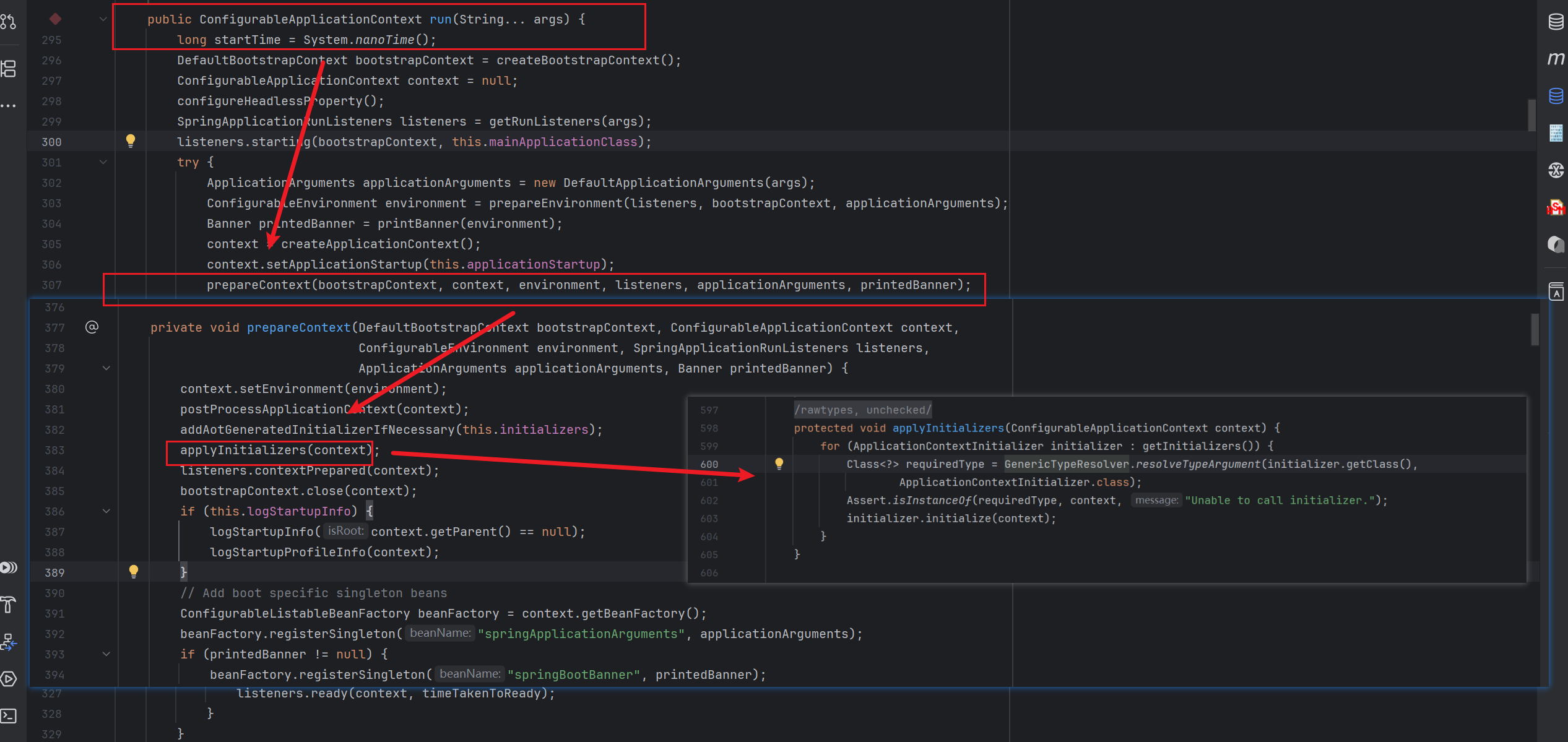
看到这里,还不明显么?SpringApplication类下的run(String... args)方法,其实就是我们所有的SpringBoot项目中,都有的启动类中的那个run方法,所以很明显,我们这个操作和项目初始化相关
我们现在再会过来看看,这个部分的到底是在干啥,看到applyInitializers,通过 for 循环遍历调用初始化器集合,会有一个 PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration初始化器,在 for 循环当中,会调用这个类的 initialize 方法来初始化配置文件。
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 循环调用初始化器
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(),
ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
initializer.initialize(context);
}
}
而在 initialize 方法中,这里就会使用到刚刚上文所提到的 PropertySourceLocator 扩展接口,SpringBoot 会拿到所有实现该接口的实现类,然后又是一个 for 循环遍历调用,而 Nacos 配置中心是有实现该接口
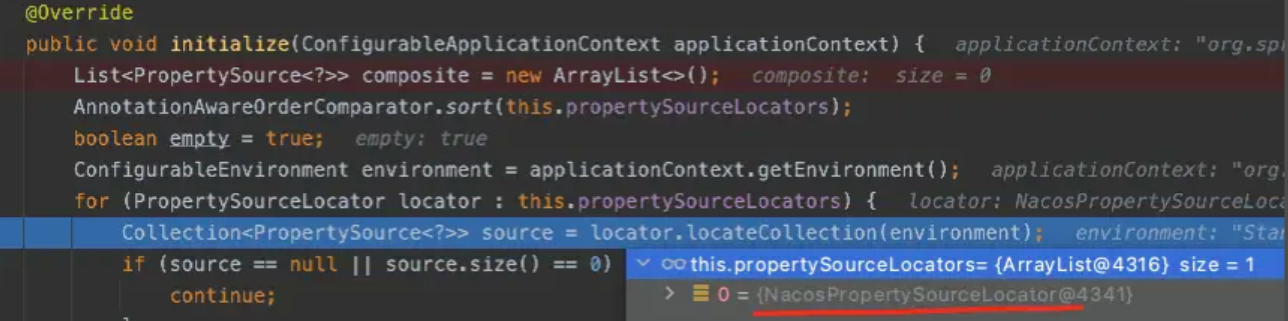
在 for 循环中,会调用 locator.locateCollection() 收集方法,在这里要绕一下,因为 PropertySourceLocator 这个扩展接口它虽然是个 interface,但是它有默认的方法实现,也就是我们最开始看到的接口中的defalut方法
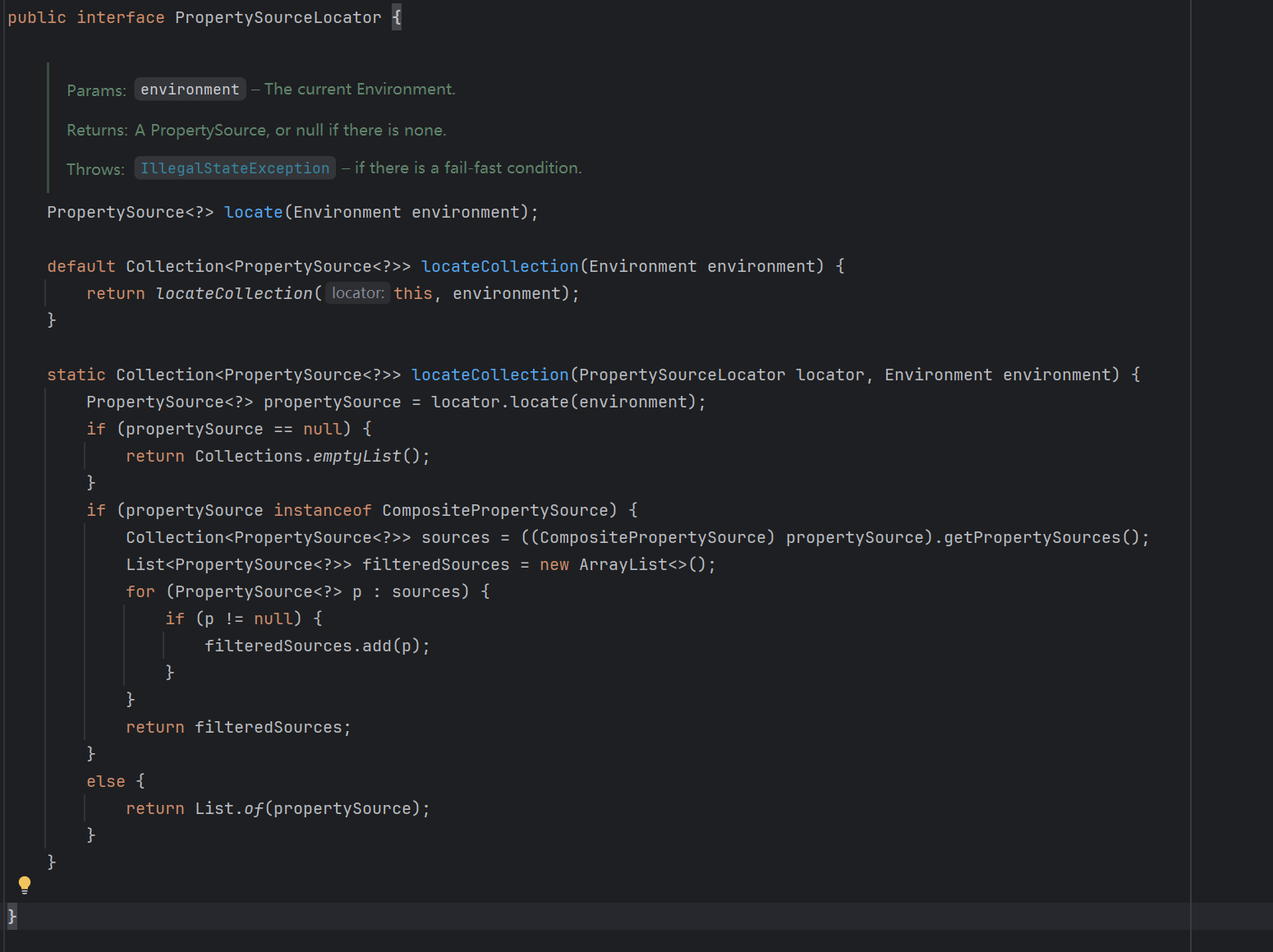
在上图的static方法中,第一行中就会调用PropertySourceLocator接口实现类的locate方法,那么因为Nacos中NacosPropertySourceLocator实现了这个接口并且在客户端的依赖中早已通过NacosConfigBootstrapConfiguration这个配置类已经生成了 NacosPropertySourceLocator这个Bean对象,自然也就是执行其中的locate方法
locate方法
这里我们直接跟核心主线任务,主要是看如何加载原创配置的。在上文源码的最后,一共加载了三个不同类型的配置文件,有些小伙伴可能没使用过这些不同类型的配置文件,这里不着急,在下一个章节中我会详细详解不同类型的配置文件的使用方式,以及配置文件的优先顺序。
public PropertySource<?> locate(Environment env) {
nacosConfigProperties.setEnvironment(env);
// 获取 configService 对象
ConfigService configService = nacosConfigManager.getConfigService();
if (null == configService) {
log.warn("no instance of config service found, can't load config from nacos");
return null;
}
// 获取 yml 配置信息
long timeout = nacosConfigProperties.getTimeout();
nacosPropertySourceBuilder = new NacosPropertySourceBuilder(configService,
timeout);
String name = nacosConfigProperties.getName();
String dataIdPrefix = nacosConfigProperties.getPrefix();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(dataIdPrefix)) {
dataIdPrefix = name;
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(dataIdPrefix)) {
dataIdPrefix = env.getProperty("spring.application.name");
}
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(
NACOS_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
// 加载共享配置文件
loadSharedConfiguration(composite);
// 加载额外的配置文件
loadExtConfiguration(composite);
// 加载自身应用配置文件
loadApplicationConfiguration(composite, dataIdPrefix, nacosConfigProperties, env);
return composite;
}
那这三个加载配置方法中,最终都会调用到 loadNacosDataIfPresent() 这个方法(这里不放图了 自己点进去看一下立马可以看到),那我们一起来看下这个方法的源码部分,代码如下:
private void loadNacosDataIfPresent(final CompositePropertySource composite,
final String dataId, final String group, String fileExtension,
boolean isRefreshable) {
// 校验参数 dataId、group
if (null == dataId || dataId.trim().length() < 1) {
return;
}
if (null == group || group.trim().length() < 1) {
return;
}
// 在这里加载 Nacos 配置文件
NacosPropertySource propertySource = this.loadNacosPropertySource(dataId, group,
fileExtension, isRefreshable);
// 把 Nacos 读取的配置添加到 Spring 容器当中
this.addFirstPropertySource(composite, propertySource, false);
}
上面代码中有使用到loadNacosPropertySource()方法,我们进入这个方法往下去,会依次调用 build() ;loadNacosData(); configService.getConfig方法,getConfig的底层是getConfigInner其源码如下
private String getConfigInner(String tenant, String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs) throws NacosException {
group = blank2defaultGroup(group);
ParamUtils.checkKeyParam(dataId, group);
ConfigResponse cr = new ConfigResponse();
cr.setDataId(dataId);
cr.setTenant(tenant);
cr.setGroup(group);
// We first try to use local failover content if exists.
// A config content for failover is not created by client program automatically,
// but is maintained by user.
// This is designed for certain scenario like client emergency reboot,
// changing config needed in the same time, while nacos server is down.
// 优先使用本地配置 主要是人为预设,最高优先级的本地配置
String content = LocalConfigInfoProcessor.getFailover(worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant);
if (content != null) {
LOGGER.warn("[{}] [get-config] get failover ok, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, config={}",
worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant, ContentUtils.truncateContent(content));
cr.setContent(content);
String encryptedDataKey = LocalEncryptedDataKeyProcessor
.getEncryptDataKeyFailover(agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant);
cr.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);
configFilterChainManager.doFilter(null, cr);
content = cr.getContent();
return content;
}
// 当本地配置没有的时候
try {
// 通过worker类来读取远程配置文件 1.4.x的版本底层就是用HTTP请求进行获取,2.x版本就是通过gRPC,通过RpcClient进行会哦去
ConfigResponse response = worker.getServerConfig(dataId, group, tenant, timeoutMs, false);
cr.setContent(response.getContent());
cr.setEncryptedDataKey(response.getEncryptedDataKey());
configFilterChainManager.doFilter(null, cr);
content = cr.getContent();
return content;
} catch (NacosException ioe) {
if (NacosException.NO_RIGHT == ioe.getErrCode()) {
throw ioe;
}
LOGGER.warn("[{}] [get-config] get from server error, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, msg={}",
worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant, ioe.toString());
}
// 远端如何获取失败的话 再次尝试本地获取 这里获取的是客户都安自动缓存的内容 仅仅在远端失败时回退上次保存的成功配置
content = LocalConfigInfoProcessor.getSnapshot(worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant);
if (content != null) {
LOGGER.warn("[{}] [get-config] get snapshot ok, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, config={}",
worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant, ContentUtils.truncateContent(content));
}
cr.setContent(content);
String encryptedDataKey = LocalEncryptedDataKeyProcessor
.getEncryptDataKeySnapshot(agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant);
cr.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);
configFilterChainManager.doFilter(null, cr);
content = cr.getContent();
return content;
}
总结
Nacos 客户端通过 Spring Boot 启动阶段的扩展机制,在应用初始化时自动从 Nacos Server 拉取配置,并依据预设的优先级策略(本地 → 远端 → 快照)确保配置可靠加载。整个过程透明、可扩展,为后续的配置热更新与动态刷新奠定了坚实基础。
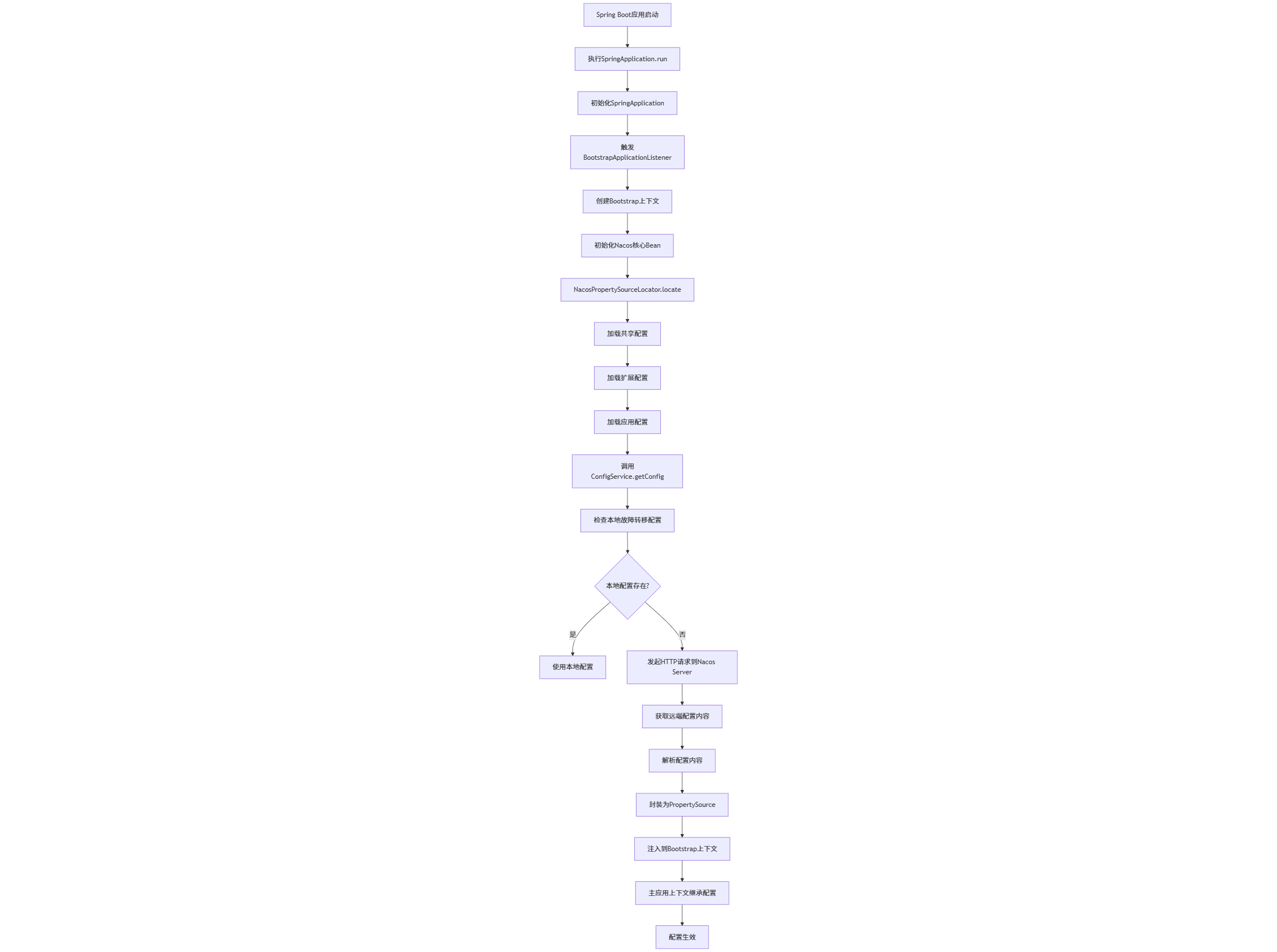
当 NacosPropertySourceLocator 的 locate 方法被调用时,它大致会做以下几件事情:
(1)获取 Nacos 配置信息:
它会从已经部分初始化的 Environment 中读取 Nacos 客户端的配置,比如 spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr、spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace、spring.cloud.nacos.config.group 等。
它还会读取需要加载的配置文件名(data-id),这可以是一个列表,支持加载多个配置文件。
(2)创建 Nacos 配置服务客户端 (ConfigService):
NacosPropertySourceLocator 会使用上面获取到的连接信息,通过 NacosFactory.createConfigService(properties) 来创建一个 ConfigService 的实例。ConfigService 是 Nacos 客户端 SDK 的核心,负责与 Nacos Server 进行网络通信。
(3)拉取配置:
NacosPropertySourceLocator 会遍历需要加载的 data-id 列表。
对于每一个 data-id,它会调用 ConfigService.getConfig(dataId, group, timeout) 方法从 Nacos Server 拉取配置内容。
Nacos 支持多种配置格式,如 properties、yaml、json 等。拉取到原始字符串后,Nacos 会根据配置的 file-extension(或文件名后缀)来选择合适的解析器(PropertySourceLoader),将其解析成一个 PropertySource 对象(例如 PropertiesPropertySource 或 YamlPropertySource)。
(4)组合并返回 PropertySource:
如果只拉取了一个配置文件,它会直接返回这个解析好的 PropertySource。
如果拉取了多个配置文件,它会将这些 PropertySource 封装到一个 CompositePropertySource(组合属性源)中,然后返回这个 CompositePropertySource。
(5)(可选 不在NacosPropertySourceLocator的相关逻辑下)注册配置监听器
如果启用了配置动态刷新功能(默认开启),NacosPropertySourceLocator 还会为每个拉取到的配置注册一个 Listener。
这个监听器会监听 Nacos Server 上对应配置的变化。当配置发生变更时,Nacos Server 会推送变更通知给客户端,监听器收到通知后会重新拉取配置,并更新 Environment 中对应的 PropertySource。
结合 @RefreshScope 注解,就可以实现 Bean 的动态刷新。
文章标题:Nacos源码学习计划-Day15-配置中心-Nacos客户端如何读取的远端配置
文章链接:https://zealsinger.xyz/?post=40
本站所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议,转载请注明来自ZealSinger !
如果觉得文章对您有用,请随意打赏。
您的支持是我们继续创作的动力!

微信扫一扫

支付宝扫一扫